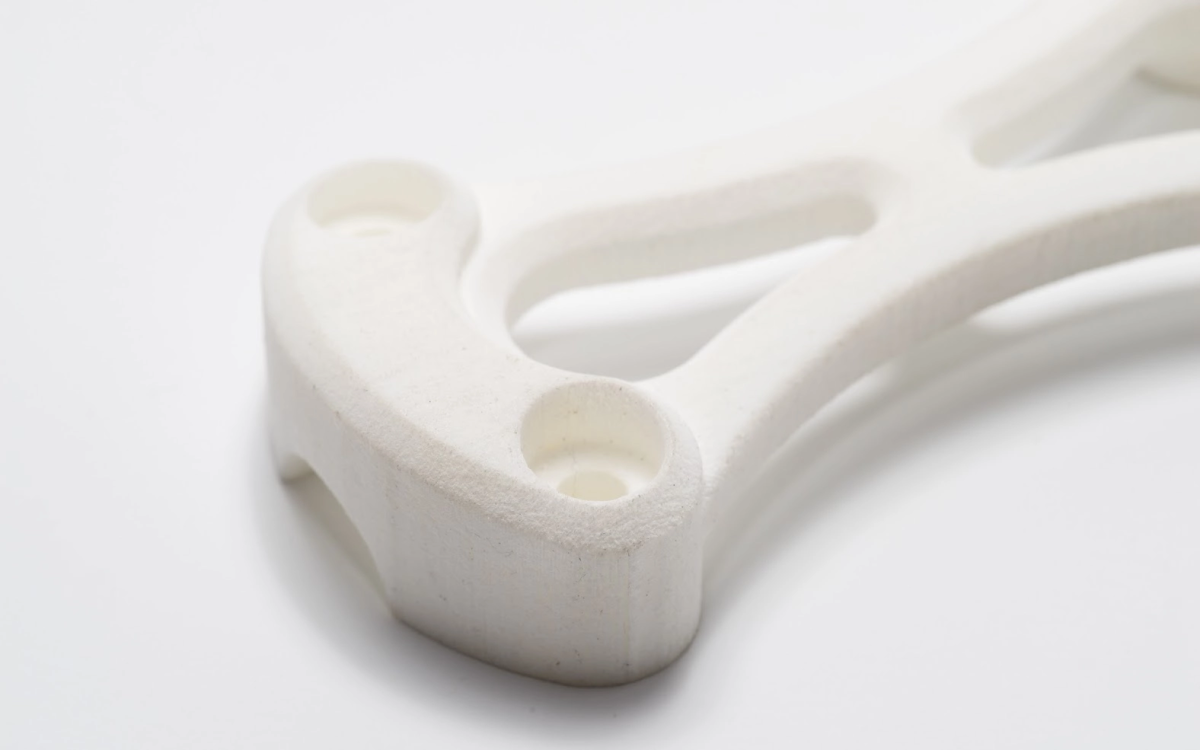
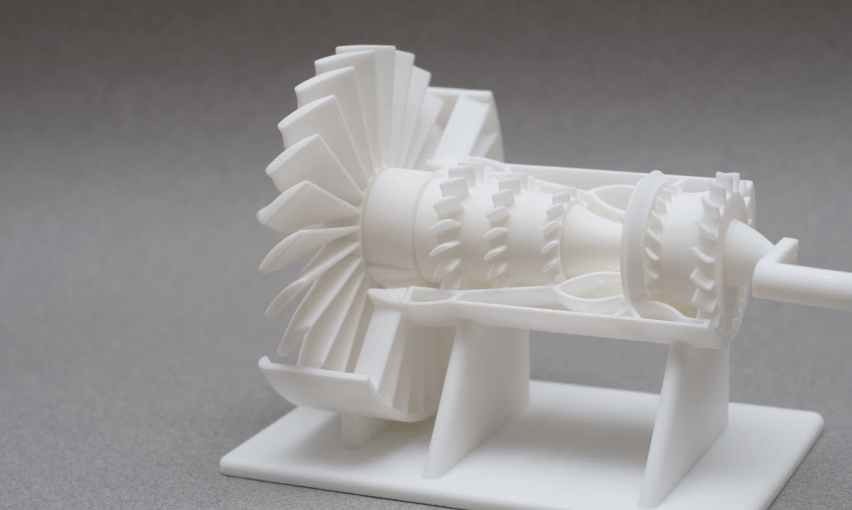
SLS 3D printing service
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D printing makes it easy to get high-quality parts for prototyping and production. Choose from industrial-grade materials and a wide range of surface finishes. Our standard lead time is just 3 working days.
SLS capabilities
| Maximum build size | Standard lead time | Dimensional accuracy | Layer thickness | Minimum feature size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 395 x 500 x 395 mm (15.53" x 19.68" x 15.53") | 3 business days | ± 0.3% with a lower limit of ± 0.3 mm (± 0.012 in) | 100μm | 0.5 mm (0.0196”) |
SLS materials
SLS 3D printing uses robust powder materials that are ideal for functional prototyping and low- to-medium volume production of end-use parts.
| Material | Color | Resolution | Tensile strength | Elongation at break | Heat deflection temperature | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nylon (PA 12) | White, dyed black | 100 μm | 41-50 MPa | 11-36% | 146-180 °C | Prototypes, detailed and complex parts, fully functional models, and end products. |
| Glass-filled Nylon (PA 12) | Off-white | 100 μm | 30-48 MPa | 6.3-9.3% | 152-179 °C | Enclosures and housings, jigs, fixtures, tooling |
SLS surface finishes
Improve the mechanical properties and aesthetic features of your SLS 3D-printed parts with these post-processing options.
How SLS stacks up against other 3D printing technologies
| Dimensional accuracy | Strengths | Build volume | Layer thickness | Min. feature size | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FDM | ± 0.5% with a lower limit on ± 0.5 mm | Low cost, wide range of materials | 500 x 500 x 500 mm (19.68" x 19.68" x 19.68") | 100-300μm | 2.0 mm (0.0787’') | ||
| Industrial FDM | ± 0.3% with a lower limit of ± 0.3 mm (± 0.012") | High level of repeatability, engineering grade materials | 406 x 355 x 406 mm (15.98” x 13.97” x 15.98") | 100-330μm | 2.0 mm (0.0787’') | ||
| Prototyping SLA | ± 0.3% with a lower limit of ± 0.3 mm (± 0.012") | Smooth surface finish, fine feature details | 145 × 145 × 175 mm (5.7" x 5.7" x 6.8") | 50-100μm | 0.2 mm (0.00787’') | ||
| Industrial SLA | ± 0.2% with a lower limit of ± 0.13 mm (± 0.005") | Smooth surface finish, fine feature details, big print area | 500 x 500 x 500 mm (19.68" x 19.68" x 19.68") | 50-100μm | 0.2 mm (0.00787’') | ||
| SLS | ± 0.3% with a lower limit of ± 0.3 mm (± 0.012”) | Design flexibility, supports not required | 395 x 500 x 395 mm (15.53" x 19.68" x 15.53") | 100μm | 0.5 mm (0.0196”) | ||
| MJF | ± 0.3% with a lower limit on ± 0.3 mm (0.012’') | Design flexibility, supports not required | 380 x 285 x 380 mm (14.9’’ x 11.2’’ x 14.9’') | 80μm | 0.5 mm (0.0196”) |
Advantages and drawbacks of SLS 3D printing
Overall, SLS printing is suitable for low-volume production and prototyping, and can print functional components and technical plastic products. However, it has a slower print speed, requires significant post-processing for surface finishing and has limitations on the maximum print size.
Advantages
Design Flexibility: SLS allows for the creation of complex geometries and intricate internal structures that may be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. It offers design freedom and enables the production of highly customized parts.
No Support Structures Required: Unlike other 3D printing technologies, SLS does not require support structures during the printing process. The powdered material surrounding the part acts as its own support, making SLS suitable for producing parts with complex geometries and internal channels.
Wide Range of Materials: SLS can work with a variety of materials, including different types of thermoplastics, metals, and even composite materials. This versatility allows for the production of functional prototypes and end-use parts with specific material properties.
Batch Production Capability: SLS is well-suited for batch production or small-scale manufacturing. Multiple parts can be printed simultaneously within the build chamber, maximizing productivity and reducing per-unit costs.
Good Mechanical Properties: SLS parts typically exhibit good mechanical properties, including strength, durability, and heat resistance. The sintering process results in parts with high density and good structural integrity.
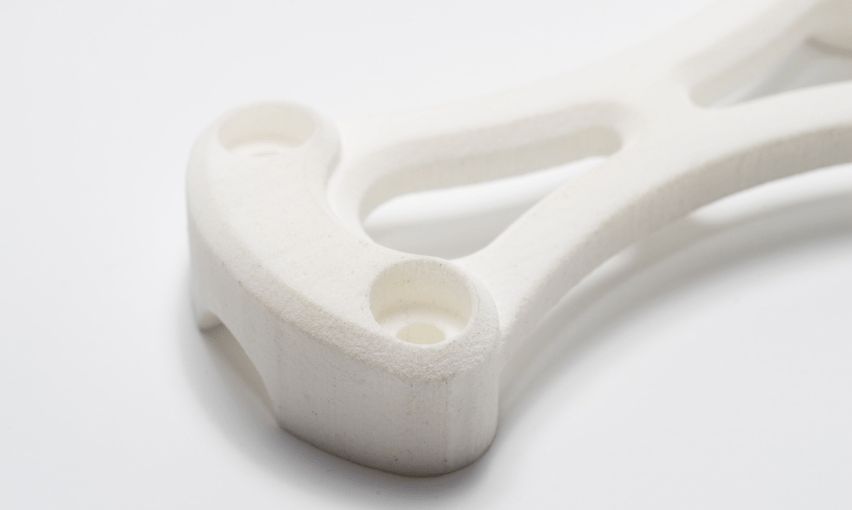

Drawbacks
Surface Finish: The surface finish of SLS-printed parts is generally rougher compared to other technologies like SLA (Stereolithography) or FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling). Additional post-processing steps may be required to achieve a smoother surface finish.
Limited Dimensional Accuracy: SLS has lower dimensional accuracy compared to some other 3D printing technologies. The accuracy can be affected by factors such as the type of material, part size, and printing parameters. Fine details and intricate features may be challenging to reproduce accurately.
Higher Equipment and Material Costs: SLS 3D printers and the associated materials can be relatively expensive compared to some other 3D printing technologies. This cost factor may limit its accessibility for certain applications or industries.
Post-Processing Requirements: After printing, SLS parts often require post-processing steps such as bead blasting, sanding, or surface treatment to improve the surface finish and remove excess powder. These additional steps can add time and labor to the overall production process.
Powder Handling and Safety Considerations: SLS involves the use of powdered materials, which require careful handling and safety precautions. The fine particles can be hazardous if inhaled, and proper ventilation and personal protective equipment are necessary when working with SLS systems.
Manufacturing standards for SLS 3D printed parts
We manufacture your custom parts according to strict manufacturing standards and ensure all parts and processes adhere to the Protolabs Network Standard. A thorough verification of these requirements is included in our inspection report that we ship with every order.
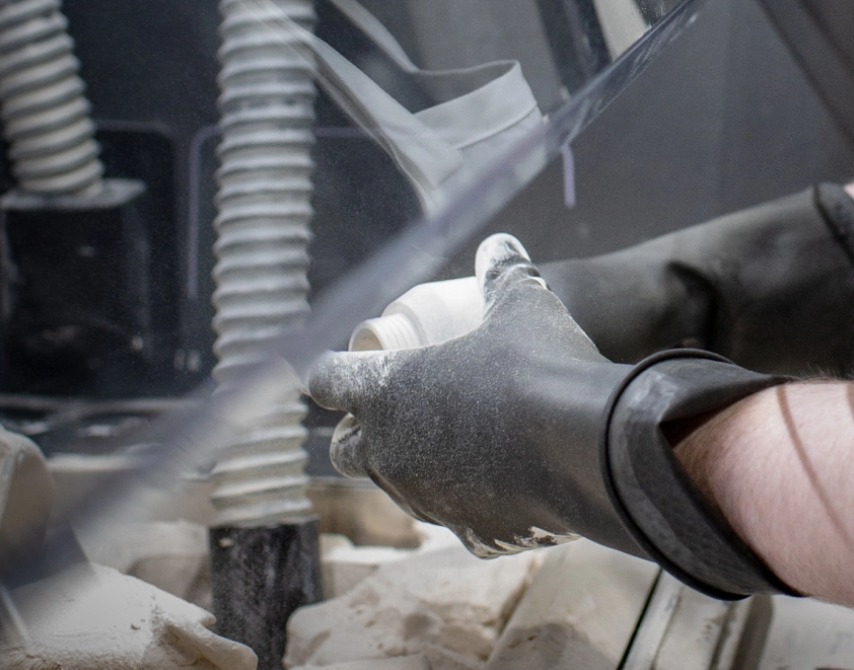
After printing, parts are bead blasted and then air blasted to get rid of the excess powder on the surface.
Additional post-processing can be done to improve part’s appearance, such as dyeing, vapor smoothing or tumbling.

Materials
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is an additive manufacturing process that belongs to the powder bed fusion family. In SLS 3D printing, a laser selectively sinters the particles of a polymer powder, fusing them together and building a part, layer by layer. The materials used in SLS are thermoplastic polymers that come in a granular form.
Overall, SLS is a versatile solution, especially if you want to hold off on injection molding and its exorbitant startup costs. It's definitely more cost-efficient for producing high-quality components in reasonable amounts (fewer than 1,000 units) to test how well your product or technology fares before making expensive molds and tools.
Our SLS 3D printing service is used for both prototyping with functional polymer components and for small to medium production runs or end-use parts. To find out more about how DTSANSE gets the most out of SLS, you can speak with an engineer by contacting dtsanse@outlook.com.